|
Music Studio |
|
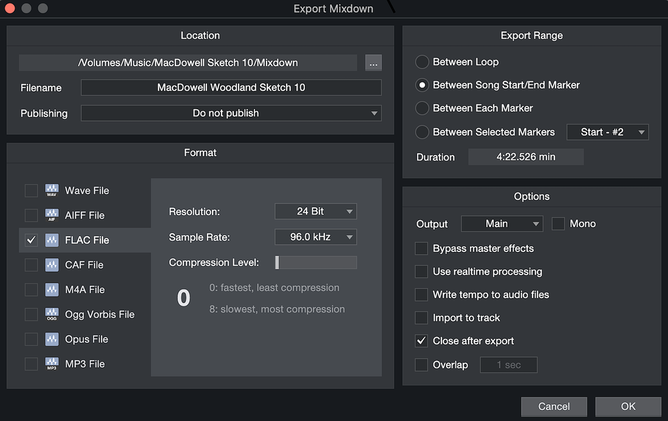
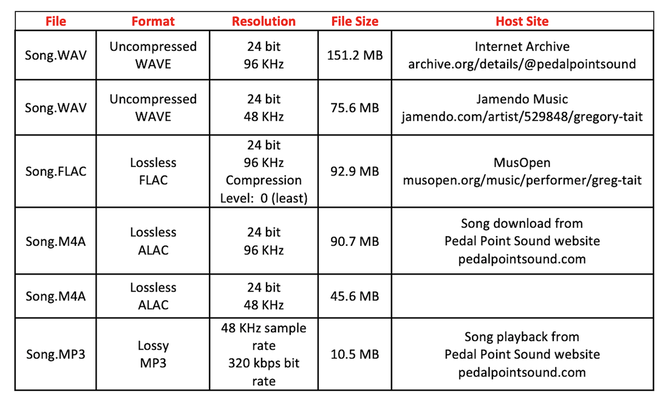
When your mixing and mastering work in the digital audio workstation (DAW) is completed, it’s time to export (save) your stereo mix to a digital audio file for distribution online or on a CD. To create an audio file in the PreSonus Studio One DAW, the “export mixdown” menu is opened, For your audio file, you can choose from a number of different digital formats. These formats can be categorized into 3 distinct groups: Uncompressed, Lossless, and Lossy. These 3 groups are summarized below. Uncompressed Uncompressed audio files are associated with professional quality sound. They have a bit depth and sampling rate of at least 16 bits and 44.1kHz, respectively. (16 bits/44.1 kHz are CD quality settings.) Therefore, you can expect at least a dynamic range of 96 dB and a frequency bandwidth of 22 kHz. Because these files are not compressed in any way, i.e., all the musical information data is kept intact, they accurately represent the master that was created. Of course, this also means song file sizes are very large. The two best formats in this category are: 1. WAV The Wave (WAV) uncompressed file format is the “go-to” file type for professional recording, mixing, and mastering. Commonly used bit depths and sampling rates are 16, 24, or 32 bits and 48, 96, or 192 kHz, in various combinations. Apple Music, Spotify, Jamendo, and many other streaming services support and sometimes even demand WAV file uploads. 2. AIFF The Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF) uncompressed file format is used on Apple’s software. Like WAV formatted files, AIFF formatted files give the highest quality audio. The AIFF format was once exclusive to Apple operating systems, but now it will play on PC operating systems too. Lossless Lossless formatted files take up significantly less storage space than uncompressed files, and ideally retain full audio quality. Lossless formatting works by compartmentalizing redundant or repeated data, while providing a “set of instructions” for these parts to be recreated during playback. As a result, lossless files are about 50% smaller in size than uncompressed files, but still offer comparable sound quality during playback. The two best formats in this category are: 1. FLAC The Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC) lossless format offers the highest quality to file size ratio of just about any other file format. It can recreate musical data as large as a 32 bit depth/192kHz sampling rate while being able to reduce file size by up to 70% in some cases ! Although FLAC is not supported by iTunes, it is supported by both Apple and PC operating systems. 2. ALAC The Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC) is Apple’s implementation of lossless data compression of digital music. ALAC encoded files have M4A filename extensions. ALAC supports audio at 16, 24, and 32 bit depths with a maximum sample rate of 384 kHz. Audio files compressed with ALAC are reduced in size by 40-60% . ALAC is supported by Apple Music. Lossy Lossy formatted files are highly compressed files that produce small file sizes. They are created by identifying and then deleting data information that is mostly indiscernible by the average listener. This is a great option for streaming, or any online service in which speed of download is more important than the quality of the audio. The sound quality of lossy files can vary greatly – from high sound quality approaching uncompressed files, to low sound quality with noticeable aliasing artifacts, quantization distortion, and attenuated high-frequency energy. The two most popular formats in this category are: 1. MP3 The most popular audio file format in use today is the ISO-MPEG Audio Level-2 Layer-3, commonly referred to as MP3. The MP3 codec compresses audio by a substantial factor, leading to very small file sizes. A wide range of compression rates can be chosen to encode/decode an MP3 file – 128, 160, 192, and 320 kbps. The 320 kbps rate offers “near CD” sound quality, with the obvious tradeoff being a larger file size. Regardless of platform, operating system, or software, an MP3 will most likely play – making it a great choice for those looking to have their music instantly playable. If you’re willing to sacrifice quality for small file size, and want ease of use and streaming capability, then MP3 is a good file format for you. 2. AAC Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is the lossy compression codec intended to replace MP3. AAC encoded audio files have AAC and M4A filename extensions. AAC employs a much more complex compression algorithm than MP3 for removing less important data information. This means that AAC offers a higher sound quality than MP3 at very similar file sizes. Since AAC can be played on almost as many platforms as MP3, it is considered the best lossy file format currently available. AAC is supported by Apple Music. -------------------------------------------------------------------- When I export a mixdown of a song, I do so creating several audio files with different formats. These audio files are destined for uploads to different hosting sites. Here’s a table listing the audio files of my piano recording of Edward MacDowell’s Woodland Sketch Op. 51, No. 10. The duration of the song is 4 minutes, 22 seconds. Apple Music will play the WAV, M4A, and MP3 files. QuickTime will play the FLAC file.
Comments are closed.
|
Categories
All
Archives
May 2023
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
